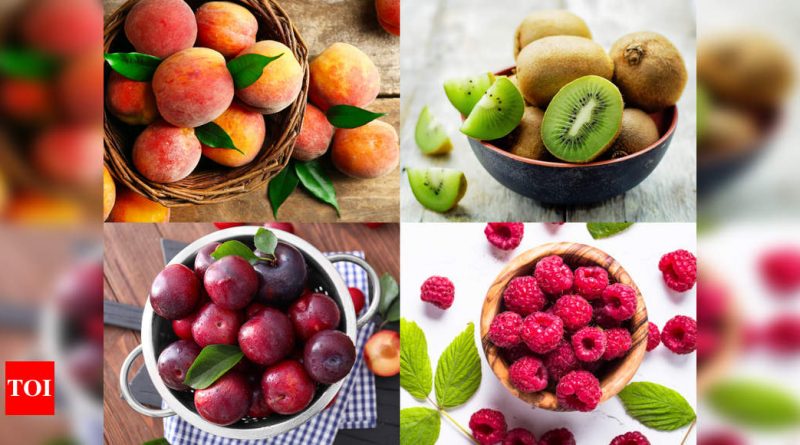
8 Low Sugar Fruits You Should Include In Your Diabetes Diet
Diabetes can affect every part of our bodies. Hence, we need to manage our blood glucose levels, also called blood sugar. Keeping our blood glucose levels in the target range is imperative to prevent or delay long-term, far-reaching health problems, such as heart disease, kidney disease and vision loss. Maintaining levels in the target range can also help improve our mood and energy. For diabetic patients, a strict diet is essential to a healthy lifestyle. Generally, blood glucose levels rise 15 minutes after a meal, reaching a peak after an hour. The most frequently seen effect of diabetes is weight loss. Therefore, a person’s goal of achieving an ideal body is often associated with restoring perfect blood glucose levels. Fruits that lower blood sugar plays an integral part in the vital dietary modifications for this process. There may be many myths surrounding the correct fruit that can lower blood sugar, but experts say eating the right fruit in moderation is the key.
Berries
Berries are very healthy and loaded with vitamins, minerals, fibres, and antioxidants. This fact makes berries one of the perfect low sugar fruits for diabetes patients. Many human studies suggest that berries can protect your cells from high blood glucose levels. They can reduce blood glucose and insulin response to high carbohydrate meals. They can also help increase insulin sensitivity.
One can eat 150 grams of pureed strawberries or mixed berries with bread, drink blueberry smoothies twice per day or take two cups of red raspberries with a high carb meal.
Avocado
Avocados, also known as butter fruit, are bright green fruit. It has a large pit and dark leathery skin. They are rich in vitamins, fibres, minerals and healthy fat. They are low in carbs and sugar and therefore very beneficial for diabetic people. A Harvard study indicates that taking a plant-based diet containing avocados can lower your chances of developing type 2 diabetes by about twenty per cent. You can take avocado pieces in a spinach salad and salmon or tuna. You can also try chickpeas with mashed avocados.
Citrus fruits
The ADA(American diabetes association) has listed citrus fruits as one of the super fruits that lower blood sugar. Fruits like lemons, grapefruits and oranges are full of folate, potassium, vitamin C and fibre. Fibres take a long time to digest. Therefore, the sugar in oranges releases slowly into the bloodstream. These fruits low in glucose also have a low glycemic index and do not affect blood glucose relatively to other fruits. You can add squeezed lemon to a glass of water to curb your appetite. You can take one grapefruit or orange with each breakfast meal.
Apple
A medium-sized apple is a great fruit choice and the best fruit to lower blood sugar if travelling. These fruits that lower blood sugar contain just 95 calories and 25 g of carbs with 4 g per medium fruit fibres. They also have vitamin C and plant compounds such as quercetin and chlorogenic acid, which help regulate blood glucose levels and shield us against diabetes. Studies indicate that eating an apple thirty mins before meals effectively reduces post-meal blood sugar.
Papaya
Papayas, also known as papaw or pawpaw, grow in tropical climates. It contains papain enzymes that aid in digestion. Is papaya good for diabetes? Yes! It has high fibre, water content and many antioxidants that help regulate blood sugar levels. Studies show that people with diabetes are also prone to other diseases such as heart diseases. The high content of potassium and vitamin content help against these diseases. Papayas can obstruct future cell damage and hence are the best fruits that lower blood sugar. When choosing to eat papaya, lookout for the fresh ones with reddish-orange skin that is soft to touch. Just scoop out the seeds and enjoy. The seeds of papaya are edible but have a bitter taste to them.
Peaches
Peaches are fuzzy fruits originating from Northwest China. Peaches are rich in beneficial vitamins, minerals and antioxidants such as vitamin C, fibre, iron and potassium. People can boost their fibre intake by replacing sweet and low fibre treats with a peach or two every day. Peaches can be eaten boiled, grilled, baked, raw, or sautéed and easily included in cold or warm dishes. Other ideas for incorporating peaches in your diet are summer salad with mixed greens or spinach and baked slices with a drizzle of honey.
Cantaloupe
Cantaloupe, commonly known as rockmelon or sweet melon, is a variety of the muskmelon family. They make a refreshing snack in the summer, having a high water content. They are also high in vitamins, minerals and antioxidants, which can help prevent cell damage that can lead to cancer and other far-reaching health conditions. Although these are delicious on their own or in a fruit salad, you can also try some of the recipes like roasted cantaloupes or cantaloupes smoothie and sorbet.
Watermelon
Watermelon is a scrambling, trailing vine-like flowering plant. It is a sweet and refreshing low-calorie summer snack. Watermelon, being high in fibre, can promote good digestive health. These fruits that lower blood sugar are also a good source of iron. The glycemic load of watermelon is low. In addition, they are also common in carbohydrates and calories. This fact helps in maintaining optimal body fat. It is best to eat watermelon without added sugars in its complete form. One should balance it with fats or proteins and avoid pairing it with high Glycemic index foods. Avoid juices and instead pair with nuts.
Conclusion
All these fruits that lower blood sugar contain significantly fewer amounts of sugar; however, consuming them in excess may shoot past your target sugar intake levels. Therefore, moderation is the key to their consumption. Most fruits contain high amounts of fibres, vitamins and minerals compared to processed sugary snacks. Fibres slow down digestion. This means our sugar may not spike so quickly after eating fruit.
Q1. What are the best vegetables for people with diabetes?
Ans: Vegetables are a central part of the diet for people with diabetes. Diabetic people should avoid food with high GI to avoid blood sugar spikes. Some good vegetables are artichoke, asparagus, broccoli, cauliflower, green beans, lettuce, eggplant, and spinach.
Q2. How does lifestyle affect diabetes?
Ans: The diabetic pandemic is most commonly associated with decreased physical activity, high energy intake, and dietary modifications leading to overweight and obesity. Studies show that lifestyle interventions like increased activity and weight loss effectively reduce diabetic progression from IGT to type 2 diabetes.