Nephrology and Kidney Disorders
What is Nephrology?
Nephrology (from the Greek ‘nephros’, meaning kidney) is a specialty branch of medicine and pediatrics related to studying normal kidney disorders function, kidney problems and their treatment, and renal replacement therapy (kidney transplants and dialysis).
Why is the Kidney Important?
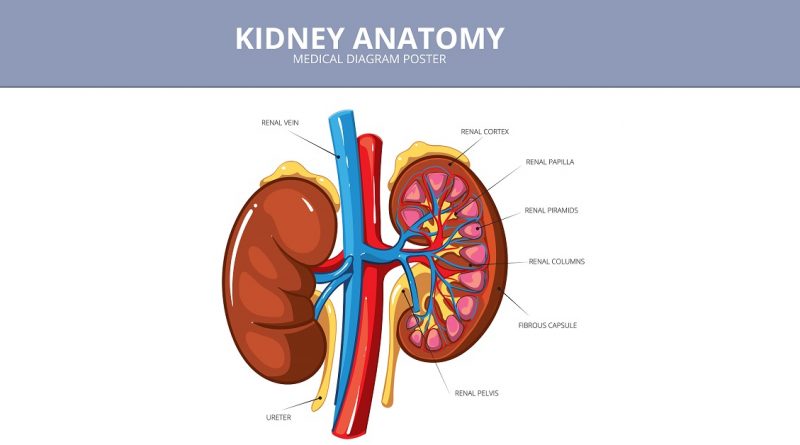
Kidneys are important excretory organs. It helps in filtering waste from the blood and discarding it from the body as urine. It also releases several crucial hormones: renin to regulate blood pressure, erythropoietin to stimulate red blood cell production, and an activated form of Vitamin D to maintain normal bone structure. Drinking plenty of water every day can prevent kidney syndromes and problems.
To get an early consultation, consider visiting the best nephrologist.
7 common kidney disorders
The kidney is susceptible to a variety of pathologies due to its unique blood supply and structure Some common kidney pathologies are:
-
Polycystic kidney disease
- This genetically acquired disease has two forms: dominant (ADPKD) and recessive (ARPKD). In the dominant form, one parent has the gene and passes it on to the child. In the recessive form, both parents pass on the affected gene to the child.
- The cysts are abnormal pouches containing fluid. Eventually, these replace normal kidney tissue and the condition gradually progresses to end-stage renal disease (ESRD).
- Symptoms include dull pain at the flanks, blood in urine, frequent UTIs, high blood pressure, and upper abdominal discomfort.
- Treatment is symptomatic. Antihypertensive can be given for high blood pressure, antibiotics for recurrent UTIs, analgesics for pain, and dialysis or transplantation for ESRD. Alternatively, surgery can be done to shrink or cut out the cysts.
-
Hypertensive nephrosclerosis
- Poorly controlled high blood pressure can cause thickening of blood vessels which can eventually lead to kidney failure.
- Symptoms include headache, giddiness, neck discomfort, fatigue, vomiting, nausea, and protein in the urine.
- Antihypertensive are the mainstay of treatment. Lowering dietary salt to less than 2g/day and daily exercise help.
-
Glomerulonephritis or glomerulosclerosis
- It is an inflammatory condition that predominantly affects the glomeruli (blood capillaries in the kidney disorders that filter blood) and causes its scarring.
- It can have three causes:
- IgA (immunoglobulin) nephropathy
- Streptococcus bacteria
- Autoimmune diseases
- Symptoms include blood and protein in the urine, frothy urine, dark-colored urine, swelling in legs, etc.
- General treatment includes medication to decrease the excretion of urinary protein, control of blood pressure, and dietary modifications.
- Specific treatment includes suppression of inflammatory processes by anti-inflammatory drugs like steroids, for example, prednisone and dexamethasone.
-
Urinary tract infection (UTI) and pyelonephritis
- Infection occurs when microorganisms attach themselves to the urethra and begin to multiply.
- This in turn may lead to infection of the kidneys called pyelonephritis. Kidney infections can go from acute to chronic in no time if left untreated. Kidney disorders failure may also result.
- Women are especially prone to get infections due to poor genital hygiene and shorter urethra.
- Risk factors for recurrent UTIs include diabetes mellitus, catheterization, abnormal urinary tract, obstructed urine flow, pregnancy, etc.
- Symptoms include painful micturition, foul-smelling urine, blood in the urine (hematuria), fever, painful lower abdomen, increased urgency to pass urine, and nausea.
- Kidney infection treatment includes appropriate antibiotics and drinking plenty of water.
-
Kidney stones
- Kidney stones start as salt or chemical crystals that precipitate in urine. This occurs when substances in urine that prevent crystallization are ineffective, or when the salts or chemicals which cause stones are more concentrated in the urine.
- The most common salt which causes kidney disorders stones is calcium oxalate stone or calcium phosphate stone. It is most commonly found in males around the age of 20 to 40 years.
- Symptoms are experienced only when the stones move inside the kidney or reach the ureter. Symptoms include extreme abdominal pain, blood in urine, painful micturition, or even anuria (complete absence of urine).
- One of the main reasons for kidney stones is consuming animal protein-based diets or taking supplements.
- Treatment includes drinking plenty of water so that the water’s force pushes out the stones. Analgesics can be used to relieve pain. Medications help to break down stones into smaller fragments. External shockwave lithotripsy (ESWL) can also be used to do this.
- Surgical intervention includes a cystoscope or open surgery (laparotomy).
-
Analgesic nephropathy
- Analgesic nephropathy is a chronic kidney disorders disease that occurs when there has been a long period of painkiller ingestion. This is usually seen in patients suffering from constant pain like cancer patients, rhabdomyolysis patients, amputees, etc.
- Analgesic nephropathy may lead to end-stage renal disease.
- Symptoms include blood and protein in the urine, vomiting, lethargy, and swelling.
- Kidney disease treatment includes avoiding long-term use of analgesics and drinking plenty of water after consuming analgesics.
-
Kidney failure or end-stage renal disease
- Occurs when the kidney disorders do not function properly or sufficiently, resulting in the accumulation of waste and toxic materials in the body.
- It may cause permanent and irreversible damage to body tissues and organs. Kidneys that perform on less than 20 percent of their capacity need renal replacement therapy.
- Risk factors for the development of ESRD include chronic diseases, inflammatory diseases, blockage of the urinary collecting system, chronic infections, and rare genetic disorders.
- Symptoms include oliguria/anuria, hematuria, nausea, vomiting, edema of hands and feet, periorbital edema, itching, sleep disturbances, loss of appetite, etc.
- Treatment of ESRD includes dialysis (hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis) and renal transplant.
- Dialysis is only a temporary procedure and needs to be done at least twice or thrice a week. The only confirmatory treatment of ESRD is a renal transplant. A transplant from siblings is usually preferred over that from parents or strangers.
If you or a loved one may need medical advice for such issues, search online for effective kidney disease treatments at the best kidney disorders transplant hospital in Coimbatore.