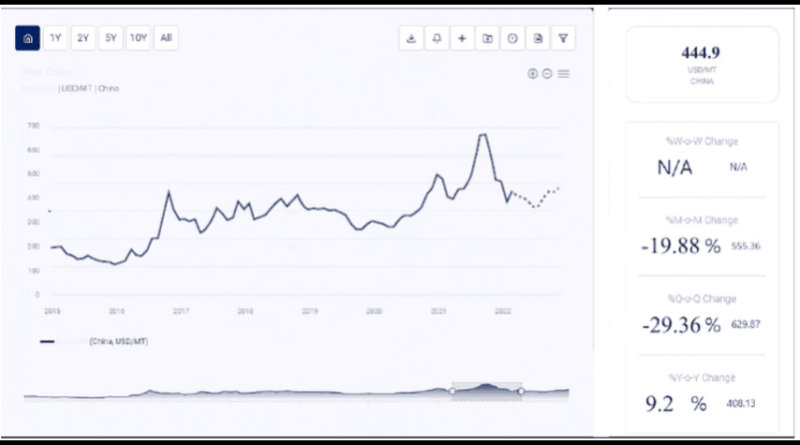
Apple Price Trend: An In-Depth Analysis
The global apple market plays a crucial role in the agricultural economy, with apples being one of the most widely consumed fruits worldwide. The price trends of apples are influenced by a variety of factors, including production levels, weather conditions, consumer demand, and international trade. This article explores the apple price trend, examining historical data, key influencing factors, and the outlook for future pricing.
1. Introduction to the Global Apple Market
Apples are a staple fruit in many households, prized for their versatility, nutritional benefits, and long shelf life. The global apple market is diverse, with major producers including China, the United States, Poland, India, and Russia. These countries contribute significantly to the global supply of apples, and their production capabilities have a direct impact on global price trends.
The apple industry is also characterized by a variety of apple varieties, each with its own demand and price dynamics. Popular varieties such as Gala, Fuji, Granny Smith, and Honeycrisp each occupy distinct market niches, influencing overall price trends.
Enquire For Regular Prices: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/apple-price-trends/pricerequest
2. Historical Apple Price Trends
Understanding the historical price trends of apples requires an analysis of data over several years, considering both global and regional factors that have impacted prices.
- Early 2000s: In the early 2000s, apple prices were relatively stable, with moderate fluctuations driven by seasonal production cycles and regional weather conditions. The global market was primarily driven by strong consumer demand in developed countries, where apples were a key component of a healthy diet.
- Mid to Late 2000s: The global financial crisis of 2008 had a notable impact on the apple market. While the demand for apples remained relatively strong due to their status as a basic food item, production costs increased due to rising energy and labor expenses. This led to slight price increases in some markets, particularly in Europe and North America.
- 2010s: The 2010s saw significant growth in apple production, particularly in China, which emerged as the world’s largest apple producer. The increased supply from China, along with advancements in storage and transportation technologies, contributed to relatively stable global prices. However, regional variations were observed, with prices in Europe and the United States experiencing some fluctuations due to weather-related crop damages and changing consumer preferences.
- COVID-19 Pandemic (2020): The COVID-19 pandemic had a mixed impact on apple prices. On one hand, the disruption of supply chains and labor shortages led to temporary price increases in some regions. On the other hand, the economic downturn reduced consumer spending power, which in some cases moderated price hikes. Overall, the pandemic highlighted the resilience of the apple market, with demand remaining strong as consumers prioritized nutritious and long-lasting food items.
3. Key Factors Influencing Apple Prices
The price of apples is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, which include:
- Weather Conditions: Apples are sensitive to weather conditions, with frost, hail, and droughts significantly impacting crop yields. Adverse weather events can lead to reduced harvests, driving up prices due to lower supply. Conversely, favorable weather conditions typically result in bumper crops, which can lead to lower prices.
- Production Costs: The costs associated with apple farming, including labor, fertilizers, pesticides, and energy, directly influence the price of apples. Rising costs in these areas often lead to higher prices for consumers.
- Varietal Demand: Different apple varieties have different levels of demand, which influences their pricing. Premium varieties like Honeycrisp and Fuji tend to command higher prices due to their unique taste and texture, while more common varieties like Red Delicious are often priced lower.
- Global Trade and Export Demand: International trade plays a significant role in apple pricing, particularly for countries that are major exporters. Trade policies, tariffs, and export restrictions can impact the global supply of apples and lead to price fluctuations. For instance, trade tensions between major producers and importers can create uncertainty in the market, influencing prices.
- Consumer Preferences: Shifts in consumer preferences, such as increased demand for organic or locally grown apples, can influence prices. Organic apples, which are grown without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers, typically command higher prices due to the additional costs associated with organic farming practices.
- Storage and Preservation: Advances in storage technology, such as controlled atmosphere storage, have allowed apples to be stored for longer periods without losing quality. This has helped stabilize prices by extending the availability of apples beyond the traditional harvest season.
4. Regional Price Trends
Apple prices vary significantly across different regions, influenced by local production capabilities, consumer demand, and trade dynamics:
- North America: The United States is one of the largest apple producers, with significant production in states like Washington, New York, and Michigan. Prices in the US are generally influenced by domestic production levels, consumer demand for specific varieties, and export demand. The rise of premium apple varieties like Honeycrisp has driven up average apple prices in recent years.
- Europe: Europe has a well-established apple market, with countries like Poland, Italy, and France being major producers. Prices in Europe are influenced by regional weather conditions, production costs, and export demand. The European market also has a strong preference for organic and locally grown apples, which can command higher prices.
- Asia-Pacific: China is the world’s largest apple producer, and its production levels have a significant impact on global prices. In the Asia-Pacific region, apple prices are influenced by domestic consumption, export demand, and competition from other fruits. Japan and South Korea are notable markets for high-quality apples, where prices tend to be higher due to consumer preferences for premium varieties.
- Latin America: In Latin America, apple production is concentrated in countries like Chile and Argentina. Prices in this region are influenced by export demand, particularly from North America and Europe. The region’s proximity to these major markets allows it to play a significant role in global apple pricing.
- Africa and the Middle East: These regions are net importers of apples, with prices influenced by import costs, exchange rates, and economic conditions. The Middle East, in particular, has a growing demand for high-quality apples, which can lead to higher prices in the region.
5. Future Outlook for Apple Prices
The future of apple prices will be shaped by a combination of factors, including:
- Climate Change: As climate change continues to impact weather patterns, apple production may become more unpredictable. Increased frequency of extreme weather events could lead to greater price volatility.
- Sustainable Farming Practices: There is growing interest in sustainable and environmentally friendly farming practices within the apple industry. While these practices may lead to higher production costs, they could also attract premium pricing in markets that prioritize sustainability.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in farming, storage, and transportation are expected to continue improving efficiency and reducing costs. However, the adoption of new technologies may also require significant investment, which could be reflected in apple prices.
- Global Trade Policies: The future of global trade policies, including tariffs and trade agreements, will play a critical role in shaping apple prices. Any changes in trade relations between major producing and importing countries could lead to price fluctuations.
- Health and Nutrition Trends: As consumers become more health-conscious, demand for apples is likely to remain strong. This could support stable or even rising prices, particularly for varieties perceived as being more nutritious or environmentally friendly.
6. Conclusion
The apple price trend is influenced by a wide range of factors, from weather conditions and production costs to consumer preferences and global trade dynamics. As the global apple market continues to evolve, stakeholders across the industry—from farmers and exporters to retailers and consumers—will need to stay informed about these trends to make strategic decisions.
Whether you’re a producer looking to optimize your supply chain, a retailer managing inventory, or a consumer seeking the best value for your money, understanding the factors that drive apple prices is key to navigating this important market. As we look to the future, the apple industry is likely to face both challenges and opportunities, with price trends reflecting the complex interplay of supply, demand, and external market forces.